


Fully machined pulleys to guarantee concentricity between parts. These consider static and dynamic balancing to eliminate vibrations in high-speed belts.
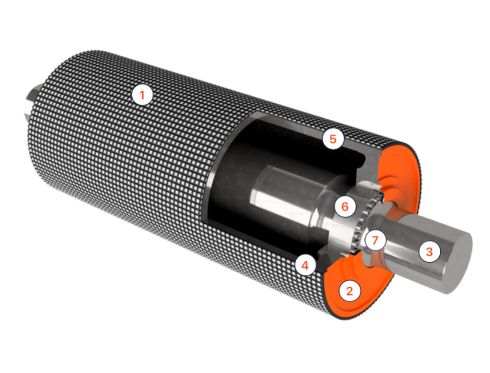
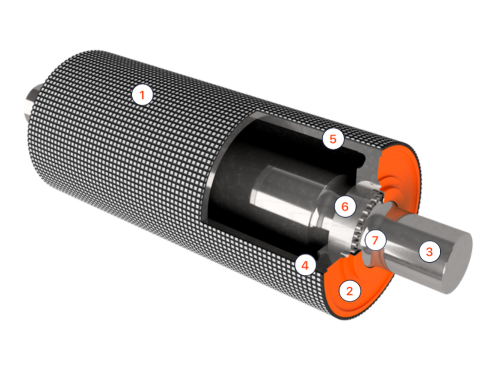
This is the natural rubber coating of the pulley shells, which is made with vulcanizing autoclaves.


The grooves depend on the pulley size and lagging thickness. This is generally used in one-way drive pulleys, in which the grooves divert water from the center of the pulley, which helps to increase adherence to the belt and keep it cleaner.
The diamond design is mainly used for reverse drive pulleys. It is also used when the rotation direction of the drive pulleys to be replaced is unknown.
These are manufactured in thicknesses from 3/8” to 1” and hardnesses from 55 to 65 Shore A.

This is a type of outer lagging, where ceramic tiles are molded into a rubber compound. This makes for excellent traction, reducing slippage and offering excellent abrasion resistance. Available in 3 thicknesses: 5/8”, 3/4”, tensions over 1500 PIW, REVESOL recommends 5/8” and 3/4”. For tensions over 700 PIW or 125 kn/mt.
| Dureza | 60+/-Shore A |
| Resistencia a la tracción en ruptura (ASTM D412) | 140kg/cm2 (mínimo) |
| Elongación en ruptura (ASTMD412) | 380%(mínimo) |
| Índice de abrasión TABER (I.A.T.) (Abrasivo S-35, carga: 1000-ciclos: 1000) | 70 máxima |
| Resistencia al desgarro (ASTM D624) | 20 kg/cm2 (mínimo) |